The Benefits of Mindful Eating for Weight Loss
What is Mindful Eating and Why is it Important?

What is Mindful Eating?
Mindful eating is a practice that encourages paying close attention to the experience of eating. It involves being present in the moment, engaging all your senses as you consume food, and becoming more aware of your body's hunger and fullness cues. This awareness goes beyond simply avoiding distractions while you eat; it's about truly connecting with your body and recognizing the signals it sends you.
Instead of mindlessly consuming food while distracted by work, screens, or other activities, mindful eating prompts you to savor each bite. This heightened awareness can lead to a deeper appreciation for the food you eat and a greater understanding of your body's needs.
Benefits of Mindful Eating
Mindful eating offers a range of benefits, including improved digestion, better body awareness, and a healthier relationship with food. By paying attention to your body's signals, you'll be better equipped to recognize when you're truly hungry and when you're satisfied. This can help you avoid overeating and support a healthier weight management strategy.
It also fosters a healthier relationship with food, moving away from emotional eating and impulsive choices. When you eat mindfully, you're more likely to choose foods that nourish your body and support your well-being, rather than succumbing to cravings or emotional responses.
The Mindful Eating Process
The process of mindful eating involves several key steps. First, find a quiet and comfortable place to eat, free from distractions. Next, observe the appearance, aroma, and texture of your food. Pay attention to the sensations in your mouth as you chew and swallow. Finally, acknowledge your feelings of hunger and fullness as you eat. This conscious engagement with the entire eating experience helps you develop a deeper connection with your body and its needs.
This intentional approach can help you make more conscious choices about what you eat, how much you eat, and when you eat, ultimately contributing to a healthier lifestyle.
Practical Applications of Mindful Eating
Mindful eating isn't just a theoretical concept; it's a practical skill that can be applied in everyday life. One simple way to incorporate mindful eating is to put your fork down between bites. This pause gives you time to savor the food and notice your body's signals. Another approach is to eat slowly and chew your food thoroughly. This process can significantly enhance your enjoyment of meals and promote better digestion.
Ultimately, mindful eating provides a framework for developing a healthier relationship with food, leading to a more balanced and fulfilling approach to nourishment.
Connecting with Your Body's Hunger and Fullness Cues
Understanding Your Body's Internal Signals
Recognizing the subtle cues your body sends regarding hunger is crucial for healthy eating habits. Paying attention to these signals allows you to eat when truly hungry and avoid unnecessary snacking or overeating. This involves more than just feeling a rumbling stomach; it encompasses a range of sensations, from mild gnawing to a more intense feeling of emptiness.
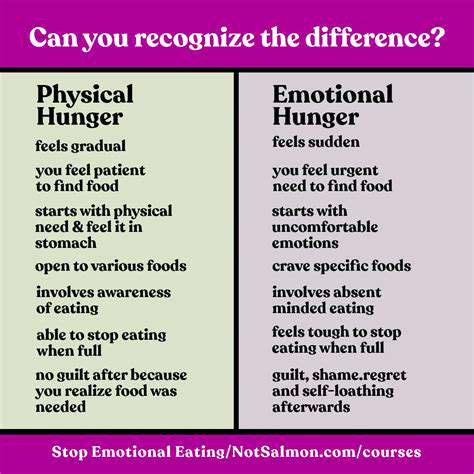
Learning to differentiate between physical hunger and emotional hunger is a key component of this process. Emotional hunger often manifests as cravings for specific foods, rather than a general feeling of emptiness. Understanding these different triggers can help you respond to your body's needs effectively.
Identifying Physical Hunger Cues
Physical hunger is characterized by a gradual onset, often starting with mild stomach contractions or a feeling of emptiness. It's essential to differentiate this from the more urgent and often intense sensations of being truly hungry. These early signals can help you anticipate your body's needs and prevent overeating.
Other physical hunger cues might include lightheadedness, a feeling of weakness, or difficulty concentrating. These signals are your body's way of telling you it needs nourishment. Learning to recognize these cues allows for more mindful eating practices.
The Role of Time in Hunger Perception
Our bodies are naturally rhythmic, and hunger often follows a predictable pattern throughout the day. Understanding your body's natural rhythm can significantly improve your ability to manage hunger and cravings, as you can anticipate when your body needs nourishment.
However, various factors, including stress, lack of sleep, and certain medications, can disrupt this natural rhythm. Recognizing these factors and their impact on your hunger cues can help you make adjustments to your eating habits.
Mindful Eating Practices for Hunger Management
Mindful eating is a valuable practice for connecting with your body's hunger signals. It encourages you to pay attention to the sensations of hunger and fullness without judgment. This practice involves slowing down your eating speed and savoring each bite.
Focusing on the taste, texture, and smell of your food can help you become more aware of your body's fullness cues. This increased awareness can help regulate your eating patterns and prevent overeating.
Emotional Eating and its Impact
Emotional eating can significantly interfere with your body's natural hunger signals. When emotional triggers drive your eating habits, it can become challenging to discern true hunger from other needs. Recognizing and addressing these emotional drivers can help you develop healthier coping mechanisms.
Stress, anxiety, and boredom can all lead to emotional eating. Understanding these triggers is crucial for developing strategies to manage these emotions without resorting to food.
Strategies for Managing Hunger Cues
Developing healthy strategies for managing hunger cues is essential for maintaining a balanced diet and overall well-being. Planning meals and snacks in advance can help you stay on track, making it less likely that you'll experience intense hunger pangs.
Staying hydrated throughout the day can also help regulate your hunger cues. Often, thirst can be mistaken for hunger, so ensuring adequate hydration is a simple yet effective step towards healthier eating habits. This can help you avoid unnecessary snacking or overeating.
The Importance of Regular Meals
Establishing a regular meal schedule can help regulate your body's hunger and fullness cues. Consuming balanced meals at consistent times can help your body develop a predictable pattern of hunger and fullness, leading to more sustainable eating habits. This can prevent drastic fluctuations in blood sugar levels, which can contribute to energy crashes and cravings.
Skipping meals can lead to overeating later, making it harder to control your hunger cues. Regular mealtimes can significantly improve your body's ability to manage hunger effectively.