Essential Vitamins for Brain Health
The B vitamin complex, encompassing various B vitamins like B6, B9 (folate), and B12, is essential for a multitude of brain functions. B vitamins are involved in the production of neurotransmitters, chemical messengers that transmit signals between brain cells. These vital messengers are crucial for processing information, regulating mood, and supporting focus and concentration. A deficiency in B vitamins can lead to neurological symptoms, impacting cognitive abilities.
Specifically, vitamin B12 is vital for the formation of myelin and the maintenance of nerve cells. A deficiency can result in neurological problems, including memory loss, confusion, and difficulty concentrating. Adequate intake of B vitamins, often found in foods like leafy greens, meat, and dairy products, is therefore critical for optimal brain health.
Vitamin C: Antioxidant Protection
Vitamin C acts as a powerful antioxidant, protecting brain cells from damage caused by free radicals. Free radicals are unstable molecules that can harm cellular structures, including those in the brain. Regular intake of vitamin C can help maintain the health of brain cells and potentially mitigate age-related cognitive decline. This antioxidant protection is vital for preserving cognitive function over time.
Vitamin D: Beyond Bone Health
Beyond its role in bone health, vitamin D plays a significant part in brain function. Research suggests a correlation between vitamin D levels and cognitive performance. Adequate vitamin D may help support memory and cognitive processes. Sunlight is a primary source of vitamin D, but dietary sources like fatty fish and fortified foods are also important. Maintaining optimal vitamin D levels is crucial for overall brain health.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Brain Building Blocks
While not technically vitamins, omega-3 fatty acids are essential for brain structure and function. These fats are vital components of brain cell membranes, influencing communication between neurons. Omega-3s support various cognitive functions, including memory and learning. Consuming fatty fish, nuts, and seeds rich in omega-3s can contribute to a healthier brain.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Building Blocks for Brain Structure
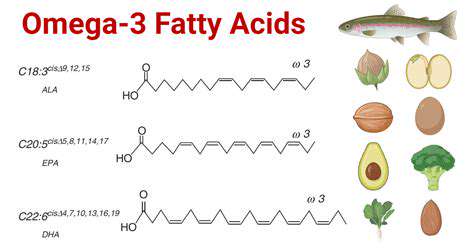
Benefits of Omega-3s for Brain Health
Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA and DHA, play a crucial role in maintaining optimal brain function throughout life. They are essential components of brain cell membranes, contributing to their structure and fluidity. Studies have shown a strong correlation between adequate omega-3 intake and improved cognitive performance, including memory and focus. This is particularly important for children and adolescents, as their brains are still developing. A healthy diet rich in omega-3s can support healthy brain development and function in these crucial stages.
Furthermore, omega-3s may help protect against age-related cognitive decline. By maintaining optimal brain cell structure and function, omega-3s can support healthy aging and reduce the risk of conditions like Alzheimer's disease and dementia. Consuming enough omega-3s throughout your lifespan is a crucial aspect of preventative health care. It's worth noting that the exact mechanisms by which omega-3s influence brain health are still being researched, but the existing evidence suggests a strong positive impact.
Omega-3s and Cardiovascular Health
Omega-3 fatty acids have demonstrated positive effects on cardiovascular health. Research suggests that they can help lower triglycerides, a type of fat found in the blood. Lowering triglycerides is important because high levels can contribute to heart disease. Omega-3s also appear to help maintain healthy blood pressure levels, which is another vital component of cardiovascular health. Maintaining healthy levels of omega-3s can contribute to overall cardiovascular wellness.
Several studies have indicated that omega-3s can reduce the risk of blood clots, which is a significant factor in heart attacks and strokes. By promoting healthy blood flow and reducing the risk of clotting, omega-3s can contribute to a healthier cardiovascular system. Incorporating omega-3s into your diet may be a valuable strategy for reducing your risk of cardiovascular disease.
Omega-3s also appear to have anti-inflammatory properties, which can further contribute to a healthier cardiovascular system. Chronic inflammation is a known risk factor for various diseases, including heart disease. Omega-3s may help reduce this inflammation, promoting overall cardiovascular health.
Omega-3s: Beyond the Brain and Heart
The benefits of omega-3 fatty acids extend beyond the brain and cardiovascular system. Preliminary research suggests a potential role for omega-3s in supporting healthy inflammation, reducing the risk of certain autoimmune diseases. Studies have also linked omega-3 intake to improved mental well-being and reduced symptoms of depression and anxiety. This is an area that warrants further investigation, but the current evidence is promising.
Moreover, omega-3s may play a role in supporting healthy joint function. Some studies indicate that omega-3s can help reduce inflammation in the joints, potentially alleviating symptoms of arthritis. While more research is needed to fully understand this connection, the potential benefits of omega-3s for joint health are notable. Furthermore, omega-3s may contribute to a healthy immune system and support overall well-being. The potential benefits of omega-3s are broad and varied, emphasizing the importance of a balanced diet rich in these essential fatty acids.
Antioxidant Vitamins: Combatting Oxidative Stress

Understanding Antioxidant Vitamins
Antioxidant vitamins play a crucial role in protecting our cells from damage caused by harmful molecules known as free radicals. These free radicals are byproducts of normal metabolic processes, but they can also originate from environmental factors like pollution and sun exposure. Excessive free radical production can lead to oxidative stress, a contributing factor in various health problems. Antioxidant vitamins, such as vitamin C and E, neutralize these free radicals, preventing them from causing cellular damage and ultimately promoting overall health and well-being. This vital protection is essential for maintaining healthy tissues and organs throughout the body.
The body doesn't produce these vital antioxidants on its own, so it's crucial to obtain them through a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and other nutrient-rich foods. A consistent intake of these vitamins helps strengthen the body's natural defense mechanisms against oxidative damage. This proactive approach can contribute to a healthier lifestyle, boosting immunity and supporting overall well-being.
Key Antioxidant Vitamins and their Roles
Vitamin C, a powerful water-soluble antioxidant, is essential for collagen synthesis, a key component of healthy skin and connective tissues. It also plays a significant role in immune function, helping the body fight off infections and maintain overall health. Vitamin C is abundant in citrus fruits, berries, and leafy green vegetables.
Vitamin E, a fat-soluble antioxidant, is primarily known for its ability to protect cell membranes from damage. This protection is crucial for maintaining healthy cell function. It also contributes to immune function and supports cardiovascular health. Good sources of vitamin E include nuts, seeds, and vegetable oils.
Dietary Sources and Potential Benefits
A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains is essential for obtaining adequate antioxidant vitamins. These nutrient-dense foods provide a wide range of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, supporting overall health and well-being. Consuming a diverse range of colorful fruits and vegetables is particularly beneficial, as different colors often indicate different types of antioxidants. This variety is essential for maximizing the benefits of these vital nutrients.
Antioxidant vitamins are associated with a reduced risk of chronic diseases, including heart disease, certain cancers, and age-related macular degeneration. A diet rich in these vitamins can contribute to the maintenance of healthy bodily functions and may help protect against the effects of aging. However, it's important to note that more research is still needed to fully understand the complex interplay between these vitamins and various health conditions.