Ketogenic Diet and Hormonal Balance

What is the Ketogenic Diet?
The ketogenic diet, often called keto, is a unique eating plan that emphasizes high-fat, moderate-protein, and minimal carbohydrate intake. By drastically cutting carbs, the body shifts from relying on glucose to burning fat for energy. This metabolic shift produces ketones, which serve as an efficient alternative fuel source.
Entering ketosis is the hallmark of this diet. In this state, your body taps into stored fat for energy, which may support weight management. Grasping these basics is essential for anyone exploring this dietary approach.
Core Principles of the Ketogenic Diet
At its heart, the keto diet demands strict carbohydrate restriction. This forces the body to adapt and seek energy elsewhere. Most keto plans limit carbs to 20-50 grams daily, though individual needs may vary.
Fat becomes the primary energy source on keto. Nutrient-dense options like avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil take center stage in meal planning.
Macronutrient Distribution
Keto follows a distinctive macronutrient profile: high fat (60-75%), moderate protein (15-20%), and very low carbs (5-10%). These percentages can be fine-tuned based on personal objectives and metabolic responses.
Precision in maintaining these ratios is crucial for sustaining ketosis. Many find that tracking their food intake helps maintain the necessary balance for optimal results.
Potential Health Benefits
Research suggests keto may offer several advantages, particularly for weight management and metabolic health. Some evidence indicates potential benefits for neurological conditions like epilepsy, though more studies are needed.
Many report successful weight management and improved metabolic markers. However, the diet's broader health impacts require further scientific exploration.
Challenges and Considerations
While promising, keto presents several practical challenges. The diet demands careful planning and may limit certain nutrient sources if not properly balanced. Some individuals experience initial difficulties adapting to the dietary restrictions.
Nutritional gaps and digestive adjustments are common concerns. Professional guidance can help mitigate these issues and ensure proper implementation.
Possible Adverse Effects
Transitioning to keto may cause temporary symptoms often called keto flu, including fatigue, headaches, or digestive changes. These typically resolve as the body adapts to its new metabolic state.
The long-term health implications of sustained ketosis remain under investigation. Medical supervision is particularly important for those with pre-existing health conditions.
Sustaining the Lifestyle
Keto requires significant commitment and lifestyle adjustments. Long-term success depends on finding sustainable approaches that fit individual preferences and routines. Combining the diet with regular physical activity enhances overall results.
Personalization is key to maintaining this eating pattern over time. Balancing dietary rigor with practical living makes the approach more manageable.
Neck discomfort often stems from multiple factors, with muscle strain being particularly common. Poor posture, repetitive motions, or awkward sleeping positions frequently contribute to muscular tension and inflammation in the neck region.
Reproductive Hormones and the Ketogenic Diet
Ketones and Female Hormones
The metabolic changes induced by keto may influence estrogen and progesterone production. Some evidence suggests potential effects on menstrual regularity, possibly through alterations in cholesterol metabolism - a key building block for steroid hormones. The relationship between ketosis and reproductive hormones remains an active area of research, with individual responses varying significantly.
Progesterone dynamics may also shift during ketosis, potentially affecting fertility and menstrual health. These changes might relate to improved insulin sensitivity, which plays a role in hormonal regulation. More comprehensive studies are needed to fully understand these complex interactions.
Testosterone Considerations
Emerging research hints at potential benefits for male testosterone levels, possibly through metabolic improvements and reduced inflammation. The mechanisms behind these effects warrant deeper investigation to establish clear cause-and-effect relationships.
For women, the impact on testosterone appears more nuanced, potentially influencing overall hormonal equilibrium. The clinical significance of these changes requires further elucidation through rigorous scientific inquiry.
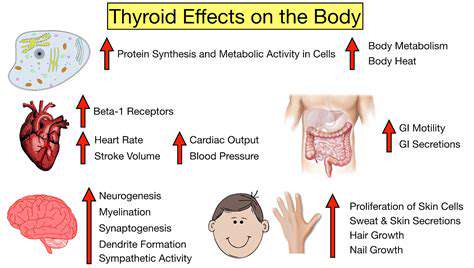
Thyroid Interactions
The thyroid's central role in metabolism makes it potentially sensitive to ketogenic dietary patterns. Some observations suggest possible effects on thyroid hormone levels, which could influence metabolic rate and other physiological processes.
Individuals with thyroid conditions should exercise particular caution and consider medical supervision when adopting keto, as the diet might interact with existing thyroid function.
Insulin's Hormonal Role
Keto's ability to enhance insulin sensitivity may have far-reaching effects on hormonal regulation. Improved insulin function could positively influence various reproductive hormones, creating potential benefits for metabolic and reproductive health.
Optimizing insulin sensitivity represents a key mechanism through which keto may affect hormonal balance. This connection underscores the importance of professional guidance when implementing the diet for hormonal concerns.
