The Glycemic Load Explained: Eating for Stable Energy
Understanding Glycemic Load
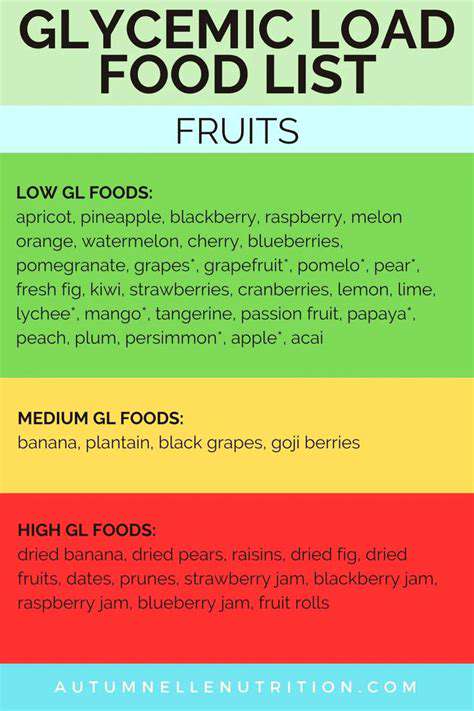
Glycemic load (GL) is a nutritional concept that takes into account both the glycemic index (GI) of a food and the amount of carbohydrate it contains. While the glycemic index focuses solely on how quickly a food raises blood sugar, GL considers the overall impact on blood glucose levels. This means that a food with a high GI but low carbohydrate content can have a relatively low GL. Understanding GL is crucial for managing blood sugar levels, especially for individuals with diabetes or those looking to maintain healthy blood glucose control. This nuanced approach to carbohydrate intake allows for a more personalized and effective dietary strategy.
A key takeaway from understanding GL is that it helps to differentiate between foods with similar GI values but different carbohydrate contents. This understanding allows for more accurate estimations of how a food will affect blood sugar, rather than relying solely on the GI. For example, a large serving of a food with a moderate GI can have a high GL, while a smaller portion might have a low GL. This intricate detail is vital for creating a balanced and effective dietary plan.
Applying Glycemic Load to Your Diet
Putting glycemic load into practice involves considering the GL of various foods and incorporating them into a meal plan. By understanding the GL of different food choices, you can create meals that promote gradual and stable blood sugar levels. This is particularly beneficial for individuals with diabetes or those seeking to improve their overall health and well-being. A diet rich in low-GL foods can lead to improved energy levels and reduced cravings for sugary foods.
Planning meals around foods with low glycemic loads is a practical strategy for managing blood sugar levels. This involves prioritizing whole grains, fruits (especially berries), non-starchy vegetables, and lean protein sources. By selecting foods that have a lower impact on blood sugar, you can promote better insulin sensitivity and overall metabolic health. Furthermore, this approach can contribute to weight management goals and reduce the risk of long-term health complications.
Choosing foods with low GL can significantly impact your overall health. By understanding the GL of different foods, you can make conscious choices that promote a healthier lifestyle. It's important to remember that portion control is essential. A large serving of a food with a moderate GL can still have a high glycemic load, so paying attention to portion sizes is critical in applying GL to your diet effectively.
Considering GL in your diet can be a valuable tool for managing blood sugar. The information can also be used to make healthy food choices when eating out or dining at social gatherings. It is important to consult with a registered dietitian or healthcare professional to create a personalized plan that aligns with your specific needs and health goals. This personalized approach is essential for ensuring that you achieve optimal results.
A complete understanding of GL will enable you to make informed food choices. This knowledge allows you to select foods that minimize blood sugar fluctuations, leading to better overall health outcomes. It is crucial to remember that GL is just one factor to consider when planning a healthy diet. A balanced approach that includes a variety of nutrient-rich foods is essential for maintaining optimal health.