The Hidden Dangers of Ultra Processed Foods
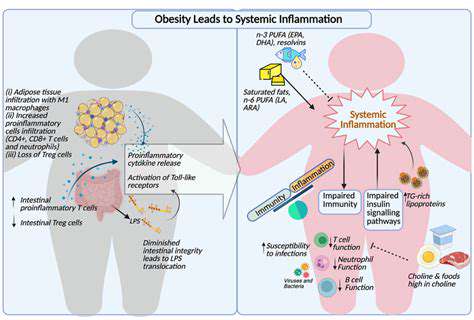
A cascade of potential health concerns can arise from prolonged exposure to environmental toxins.
Long-term contact with environmental pollutants, including heavy metals, pesticides, and industrial chemicals, may trigger numerous health complications. These substances tend to build up in bodily tissues gradually, possibly interfering with normal biological functions and elevating the likelihood of persistent illnesses. Grasping how these contaminants cause damage at the cellular level proves essential for creating meaningful protective and therapeutic approaches.
The consequences of toxic environmental elements appear in diverse forms, influencing several bodily systems. Certain air pollutants, for instance, can harm lung tissue, resulting in respiratory conditions including asthma and persistent bronchial inflammation. Some neurotoxic compounds might impair cognitive function and motor skills. The gradual nature of symptom development from sustained exposure frequently makes timely identification and treatment particularly difficult.
Vulnerable groups often face heightened risks.
Demographics such as young children, expectant mothers, and senior citizens typically demonstrate increased sensitivity to environmental toxins. Developing children, with their immature physiological systems, show particular susceptibility to these chemical threats. Their greater exposure comes from frequent contact with tainted surfaces and consumption of contaminated substances. Implementing rigorous environmental safeguards becomes paramount to shield these at-risk groups from harm.
Additionally, economic circumstances significantly influence exposure patterns. Residents of disadvantaged neighborhoods frequently inhabit areas with elevated pollution levels and have fewer resources to counteract exposure effects. This environmental injustice creates unequal health burdens across communities. Developing focused solutions to these inequities represents a critical step toward fair health outcomes.
Proactive protection and community health initiatives prove essential.
Establishing comprehensive environmental policies and encouraging eco-friendly alternatives helps reduce toxin-related dangers. Such efforts might include rigorous industrial emission controls, tighter restrictions on agricultural chemicals, and advocacy for less hazardous substitutes. Community education programs serve an important function in raising awareness about risks and promoting safer practices. Simple actions like choosing reusable containers instead of plastic products can decrease chemical exposure.
Supporting scientific investigations into the prolonged consequences of specific environmental toxins remains equally important. These studies can guide the creation of targeted prevention methods and specialized treatments for toxin-associated conditions. Enhancing surveillance systems and data analysis capabilities enables better tracking of environmental hazards, identification of new threats, and refinement of public health strategies.
Our genetic heritage substantially influences both physical characteristics and behavioral patterns, creating deep familial connections. The resemblances we observe among relatives—whether in physical features, personality traits, or disease susceptibility—frequently stem directly from inherited genetic patterns. These biological instructions, transmitted across generations, can provide insights about our lineage and potential medical vulnerabilities.
Beyond the Buzzwords: Making Informed Choices for a Healthier Future
Decoding the Science Behind Popular Claims
The wellness sector continues expanding rapidly, saturated with countless products, regimens, and bold assertions. Between extraordinary nutritional supplements and extreme fitness programs, consumers face considerable confusion when evaluating options. However, thoughtful self-care demands comprehension of the underlying scientific principles rather than superficial claims. Rather than following marketing hype, we must prioritize solutions with empirical support. This means examining supplement formulations critically, understanding exercise physiology thoroughly, and seeking professional medical guidance for individual needs.
Cultivating better health shouldn't involve blind trust but rather careful consideration of scientifically validated methods. This process requires inquisitiveness, reliance on trustworthy references, and ultimately choosing evidence-based approaches over sensationalized claims regarding personal wellness.
Evaluating Information Sources Critically
While digital platforms provide abundant data, quality varies significantly. Identifying authoritative sources separates valuable knowledge from misinformation. Prioritize websites with institutional domains (.org, .edu). Verify reference lists and author qualifications. Compare data across multiple reliable outlets. Approach personal success stories cautiously, as these may not represent typical outcomes or scientific agreement.
Sharpening analytical abilities when assessing health information helps avoid common errors. This includes recognizing study limitations and distinguishing between coincidental relationships and proven cause-effect connections. Taking responsibility for thorough research and verification enables decisions that truly support health objectives.
Embracing Comprehensive Wellness
Authentic health extends beyond physical condition alone. It acknowledges the fundamental links between mental state, physical being, and emotional balance. Supporting psychological health through meditation techniques, maintaining meaningful relationships, and pursuing enjoyable activities all contribute to complete wellbeing.
Customizing Your Health Strategy
No universal solution exists for achieving wellness. Effective methods vary significantly between individuals. Recognizing personal requirements, constraints, and preferences remains crucial. This involves bodily awareness, identification of individual stress factors, and willingness to modify approaches as circumstances change. Professional consultations with medical providers, diet specialists, or other experts can tailor health plans to specific situations, offering customized recommendations and assistance.
Personal adaptation facilitates creation of maintainable, rewarding wellness pathways rather than temporary fixes. This individualized method guarantees that efforts match unique circumstances and abilities, promoting lasting benefits and enhanced quality of life.