Ketogenic Diet Side Effects and How to Manage Them
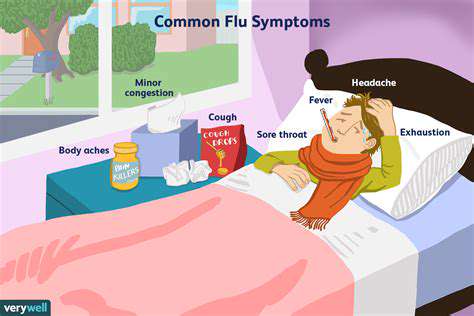
Initial Keto Flu Symptoms: A Deep Dive
When transitioning to a ketogenic diet, many people experience what's commonly called the keto flu. This temporary set of symptoms, often beginning within the first few days or weeks, can feel challenging but is typically short-lived. The key to success lies in recognizing these symptoms early and knowing how to handle them properly. It's worth noting that everyone's experience differs - some barely notice any changes while others face more pronounced effects.
Common complaints include headaches, fatigue, and occasional nausea. These reactions occur as your body switches from burning carbohydrates to using fat as its primary energy source. While generally harmless, if symptoms become severe or last beyond a few weeks, consulting a healthcare provider is strongly advised.
Common Keto Flu Symptoms and Their Potential Causes
Fatigue often tops the list of complaints. This isn't surprising since your body needs time to adapt to its new fuel source. The transition can leave you feeling drained as your metabolism rewires itself. Electrolyte imbalances, particularly involving sodium and potassium, frequently contribute to this tired feeling.
Headaches frequently appear during this adjustment period. They typically stem from dehydration or electrolyte disturbances that occur as your body flushes out excess water. Drinking plenty of fluids becomes particularly important during this phase.
Some individuals report nausea, though this tends to be less common. This discomfort usually passes as your system becomes accustomed to ketosis. For those experiencing persistent vomiting or severe nausea, medical advice should be sought promptly.
Muscle cramps and constipation may also occur. These often relate to electrolyte imbalances or reduced fiber consumption. Increasing water intake and ensuring proper mineral balance can provide relief. Maintaining balanced nutrition remains the cornerstone of managing these transitional symptoms effectively.
Addressing the Keto Flu: Strategies for Management
Hydration deserves special attention during this transition. Drinking ample water throughout the day helps compensate for increased fluid loss. Electrolyte supplements or mineral-rich foods can further support your body's adjustment process.
Gradual dietary changes prove easier on your system than abrupt shifts. Slowly reducing carbohydrates while increasing healthy fats gives your body time to adapt without shock. This measured approach often results in fewer and less severe symptoms.
Don't underestimate the power of rest and stress management. Adequate sleep and relaxation techniques help your body handle metabolic changes more smoothly. Tuning into your body's signals and responding appropriately makes the transition far more manageable.
Addressing Digestive Issues: Constipation and Other Concerns
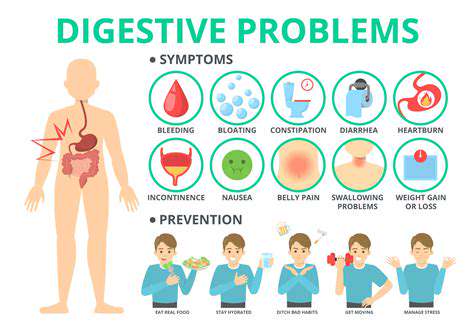
Understanding the Root Causes of Digestive Problems
Digestive discomfort can arise from multiple factors, ranging from dietary choices to stress levels. Identifying the specific triggers in your case is the first step toward finding relief. Often, several contributing elements combine to create digestive disturbances, requiring a multifaceted solution.
Modern diets heavy in processed foods and low in fiber frequently disrupt digestive function. These dietary patterns can lead to various issues including irregular bowel movements and bloating. Adjusting your eating habits forms the foundation of digestive wellness.
Dietary Adjustments for Improved Digestion
Increasing fiber intake through fruits, vegetables, and whole grains typically improves bowel regularity. These natural foods provide the bulk needed for healthy digestion while supplying essential nutrients.
Identifying and eliminating problematic foods often brings significant relief. Paying attention to how your body responds to different foods allows for personalized dietary tweaks that maximize comfort. Common irritants include dairy, spicy foods, and caffeine for many individuals.
The Role of Lifestyle Factors in Digestive Health
Regular physical activity benefits digestion by stimulating intestinal movement. Even moderate exercise can make a noticeable difference in digestive comfort and regularity.
Stress management techniques deserve special consideration. Chronic stress directly impacts gut function, often exacerbating digestive complaints. Practices like deep breathing or gentle yoga can help restore digestive balance when practiced consistently.
The Importance of Hydration in Digestive Function
Water plays a critical role in digestive processes. Proper hydration ensures smooth passage of food through your system and prevents uncomfortable constipation. This simple yet vital aspect of health often gets overlooked in digestive care.
Seeking Professional Medical Advice for Persistent Issues
While lifestyle changes help many digestive complaints, persistent problems warrant professional evaluation. A gastroenterologist can identify potential underlying conditions requiring specific treatment.
Ignoring ongoing digestive symptoms may allow manageable issues to develop into more serious concerns. Timely medical consultation provides peace of mind and appropriate care when needed.
Exploring Complementary and Alternative Therapies
Some people find relief through complementary approaches like probiotics or herbal remedies. These options may support conventional treatments when used appropriately.
Always discuss alternative therapies with your healthcare provider before beginning, especially if you have existing health conditions. This ensures safe integration with your overall care plan.
Potential Nutritional Deficiencies and How to Avoid Them