Moxibustion for Joint Pain: Warming Therapy

How Does Moxibustion Work for Joint Pain?

Moxibustion's Mechanism of Action
This traditional Chinese healing method utilizes the burning of mugwort, a medicinal herb, applied near or directly on strategic acupoints across the body. The therapeutic warmth generated penetrates deep into tissues, activating these energy points to enhance circulation and restore vital energy pathways. Practitioners observe this process helps diminish discomfort while potentially rebalancing the body's internal systems.
While modern science continues exploring exact physiological mechanisms, several compelling theories have emerged. The thermal stimulation appears to activate sensory nerves, prompting the release of endogenous opioids - the body's natural pain-modulating chemicals. Alternatively, the localized heat may enhance vascular activity, reducing inflammatory markers while accelerating tissue regeneration processes.
Effects on Inflammation and Pain
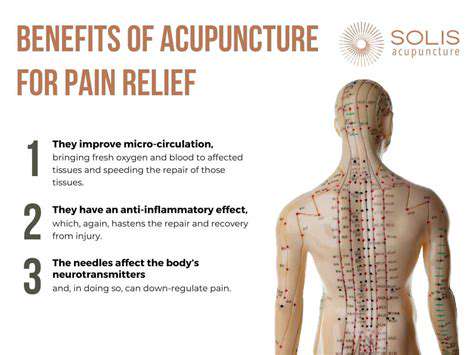
Clinical applications frequently target inflammatory disorders and chronic pain syndromes. The penetrating warmth from smoldering mugwort demonstrates vasodilatory effects, potentially decreasing inflammatory mediators while improving lymphatic drainage. This dual action may simultaneously reduce nociceptive signaling along neural pathways.
Emerging research indicates moxibustion may influence pain perception through modulation of neurotransmitter systems and inflammatory cytokines. While promising, further controlled studies are required to establish standardized treatment parameters for various musculoskeletal conditions.
Stimulation of Acupoints and Energy Flow
Traditional Chinese medicine conceptualizes the body as an interconnected network of energy channels (meridians). Moxibustion therapy specifically targets acupoints along these pathways, using thermal energy to activate and regulate Qi flow. This stimulation is believed to correct energetic imbalances that manifest as physical symptoms.
The therapeutic warming of acupoints may produce systemic effects beyond local treatment sites. By removing energetic blockages, practitioners observe improved physiological function and enhanced self-regulatory capacity throughout the entire meridian system.
Potential Benefits for Joint Pain Relief
Historical applications extensively document moxibustion for arthralgia and joint stiffness management. The deep-penetrating heat promotes muscular relaxation while increasing synovial fluid circulation. Enhanced perfusion facilitates nutrient delivery and metabolic waste clearance in periarticular tissues.
Centuries of empirical evidence support moxibustion's role in managing arthritic conditions, though contemporary research methodologies are needed to quantify its therapeutic value. Many patients report noticeable improvements in joint mobility and discomfort following consistent treatment protocols.
Safety and Considerations
When administered by trained specialists, moxibustion demonstrates an excellent safety profile. Certain populations require special consideration, including individuals with thermoregulatory disorders, dermal sensitivities, or cardiovascular conditions. A thorough health assessment should precede any treatment regimen.
Proper application technique minimizes risks of thermal injury. Patients should exclusively seek treatment from licensed practitioners with extensive experience in traditional Chinese medicine modalities. Appropriate ventilation and fire safety measures are essential during treatment sessions.
Potential Benefits for Joint Pain Relief
Promoting Circulation
The gentle thermal stimulation of moxibustion induces localized vasodilation, enhancing microcirculation in affected joints. Improved vascular perfusion facilitates oxygen and nutrient delivery while accelerating the removal of inflammatory metabolites. Patients often describe a comforting warmth that gradually spreads through the treated area, accompanying reduced stiffness and improved mobility.
These circulatory benefits frequently extend beyond the immediate treatment zone, potentially creating systemic improvements in peripheral circulation. Many recipients report enhanced overall vitality and reduced generalized stiffness following regular sessions.
Reducing Muscle Tension
Chronic joint dysfunction commonly precipitates compensatory muscular hypertonicity. Moxibustion's deep-penetrating warmth helps relax contracted musculature through thermoreceptor-mediated mechanisms. The gradual heat application reduces gamma motor neuron activity, thereby decreasing muscle spindle sensitivity.
As periarticular muscles relax, patients typically experience improved range of motion and decreased mechanical stress on affected joints. This muscular normalization often allows for more fluid, natural movement patterns with reduced discomfort.
Managing Inflammation
The modality's thermal effects appear to modulate inflammatory cascades through several pathways. Local temperature elevation may inhibit pro-inflammatory cytokine production while stimulating anti-inflammatory mediators. Improved vascular and lymphatic circulation enhances the clearance of inflammatory exudates from affected tissues.
Chronic inflammatory states can create systemic metabolic disturbances. By addressing localized inflammation, moxibustion may contribute to broader improvements in physiological homeostasis and overall wellbeing.
Boosting the Immune System
Emerging evidence suggests controlled thermal stress from moxibustion may stimulate immune-modulatory responses. The mild heat shock appears to activate heat shock proteins and other cellular stress response elements. This low-grade stimulation may enhance local immune surveillance while supporting tissue repair mechanisms.
Enhancing Pain Relief
Moxibustion addresses nociception through multiple convergent mechanisms. The combined anti-inflammatory, circulatory, and neuromuscular effects create a comprehensive approach to pain management. Many patients report sustained relief that surpasses isolated symptomatic treatments.
The therapy's warmth triggers endogenous opioid release while potentially modulating pain gate mechanisms in the central nervous system. This natural analgesic effect complements the modality's other physiological actions for comprehensive pain control.
Potential Benefits for Specific Joint Conditions
While beneficial for generalized arthralgia, moxibustion shows particular promise for degenerative and autoimmune joint conditions. The therapy may help preserve joint function in osteoarthritis by improving cartilage nutrition. In rheumatoid arthritis, its immunomodulatory potential could complement conventional treatments.
Current research continues to explore moxibustion's role in various arthropathies. Preliminary data suggest it may help slow disease progression while improving quality of life markers in chronic joint disorders.
Safety and Considerations

Safety Precautions
Implementing comprehensive safety measures forms the foundation of responsible moxibustion practice. Meticulous attention to treatment protocols and patient screening ensures optimal therapeutic outcomes while minimizing risks. Practitioners must thoroughly evaluate individual health histories, identifying any contraindications or special considerations. Proper training in both traditional techniques and modern safety standards is essential for delivering effective, risk-adjusted care.
A detailed risk assessment should precede every treatment session. Identifying potential complications, from mild thermal discomfort to rare hypersensitivity reactions, allows for appropriate precautionary measures. Clear communication regarding expected sensations and potential side effects helps establish realistic patient expectations. Maintaining sterile equipment and proper ventilation further enhances treatment safety.
Environmental Considerations
Contemporary practice emphasizes environmentally sustainable approaches to traditional medicine. Responsible sourcing of mugwort and other herbal materials supports ecological balance while ensuring product quality. Implementing energy-efficient practice methods demonstrates commitment to both patient care and environmental stewardship.
Waste reduction strategies, including proper disposal of used moxa materials, minimize the ecological footprint of clinical practice. Many practitioners now incorporate recycled or biodegradable materials into their treatment protocols. These environmentally conscious approaches align traditional healing with modern sustainability principles.
Emergency Preparedness
Comprehensive emergency protocols are essential for any clinical setting offering thermal therapies. Developing specific response plans for potential complications, from minor burns to rare allergic reactions, ensures prompt appropriate intervention. Regular staff training in emergency procedures maintains preparedness for any unforeseen events.
Treatment areas should contain clearly marked emergency equipment, including burn care supplies and first aid materials. Periodic safety drills help staff maintain proficiency in handling thermal injuries or other treatment-related emergencies. Establishing clear emergency communication channels with local medical facilities facilitates coordinated care when needed.