Paleo Diet for Autoimmune Conditions: A Deep Dive
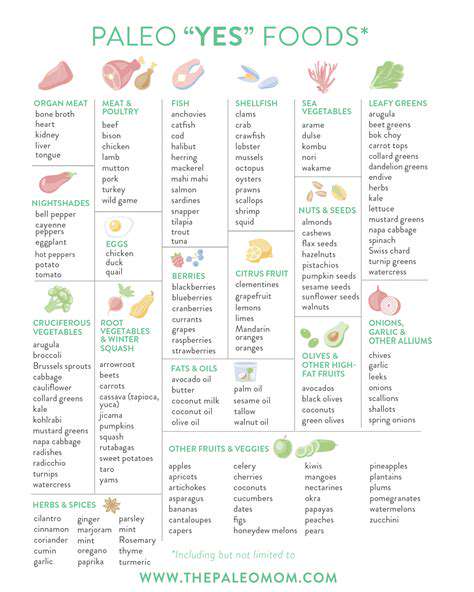
Potential Benefits for Autoimmune Conditions
Potential for Reduced Inflammation
One of the key potential benefits of the Paleo diet for autoimmune conditions lies in its anti-inflammatory properties. Many autoimmune diseases are characterized by chronic inflammation, and the Paleo diet's emphasis on whole, unprocessed foods, rich in antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds, may help to mitigate this. By reducing the intake of inflammatory foods like processed grains, dairy, and refined sugars, the Paleo diet can potentially lessen the body's inflammatory response, which can be crucial in managing autoimmune symptoms.
Studies suggest that certain foods, such as those high in omega-3 fatty acids found in fatty fish and nuts, can have a positive impact on reducing inflammation. The Paleo diet, by encouraging the consumption of these foods, may provide the body with the necessary nutrients to combat inflammation, thereby potentially alleviating symptoms associated with autoimmune conditions.
Improved Gut Health
The Paleo diet's focus on whole, unprocessed foods, particularly fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins, can significantly contribute to better gut health. A healthy gut microbiome is crucial for overall well-being, and its disruption has been linked to various autoimmune diseases. By providing the gut with beneficial bacteria through fermented foods and high-fiber foods, the Paleo diet may help restore gut balance, which is essential for preventing and managing autoimmune conditions.
The elimination of processed foods, refined sugars, and excessive amounts of saturated fats often found in typical Western diets can also contribute to a healthier gut environment. This improved gut health can potentially reduce the risk of leaky gut syndrome, a condition that allows undigested food particles to leak into the bloodstream, triggering an inflammatory response and exacerbating autoimmune symptoms.
Nutrient Rich Food Sources
The Paleo diet emphasizes nutrient-rich foods like fruits, vegetables, lean meats, and healthy fats. These foods provide the body with essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants crucial for supporting a healthy immune system. A balanced intake of these nutrients is vital for maintaining overall health and potentially mitigating the effects of autoimmune conditions.
The focus on whole foods in the Paleo diet can also help ensure a more balanced intake of micronutrients, which often get overlooked in processed food-centric diets. This can be particularly important for individuals with autoimmune diseases, as their bodies may have increased nutritional needs due to the inflammatory processes involved.
Reduced Exposure to Potential Triggers
Autoimmune conditions often involve an overactive immune response targeting the body's own tissues. The Paleo diet, by eliminating many common food triggers, may help reduce the body's exposure to potential antigens that can exacerbate these responses. Removing gluten, dairy, and other processed foods from the diet can potentially lessen the inflammatory burden on the body and reduce autoimmune symptoms.
By avoiding these potential triggers, the diet may allow the immune system to focus on its proper function rather than reacting to foreign substances, potentially leading to a reduction in the frequency and severity of autoimmune symptoms.
Potential for Weight Management
Weight management is an important aspect of managing many autoimmune conditions. The Paleo diet, by focusing on whole, unprocessed foods and minimizing processed foods, can be beneficial for weight loss or maintenance, especially when combined with regular exercise.
The emphasis on fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins generally results in a more nutrient-dense, lower-calorie diet, which can contribute to weight management. This, in turn, can have a positive impact on overall health and potentially reduce the burden on the body's immune system, allowing for better management of autoimmune conditions.
Potential Risks and Considerations
Potential Nutritional Deficiencies
A strict paleo diet, while potentially beneficial for some autoimmune conditions, can also pose risks if not carefully planned and monitored. A significant concern is the potential for nutritional deficiencies. The paleo diet often restricts or limits certain food groups, like dairy and grains, which are excellent sources of essential vitamins and minerals. Without careful supplementation or a wide variety of other food choices, individuals could experience deficiencies in calcium, vitamin D, iron, or certain B vitamins. This is particularly important for individuals with pre-existing nutritional needs or those following the diet for an extended period.
Careful consideration of food choices and potential supplementation is crucial to mitigate these risks. A registered dietitian or healthcare professional can help assess individual needs and guide appropriate dietary modifications.
Gastrointestinal Issues
Some individuals may experience digestive issues like bloating, gas, or diarrhea when transitioning to a paleo diet, particularly if they are not gradually introducing new foods. The high fiber content in certain paleo-friendly foods, like vegetables and fruits, can sometimes cause digestive distress, particularly for those not accustomed to a high-fiber diet. Additionally, eliminating entire food groups can disrupt the gut microbiome, which plays a vital role in overall health and digestion.
Gradually introducing new foods and paying attention to individual tolerance levels can help mitigate these digestive issues. Hydration is also crucial for optimal digestion on any diet, especially one with a high fiber content.
Potential for Social Isolation
Following a restrictive diet like the paleo diet can sometimes lead to social isolation, especially when dining out or attending social gatherings. Finding paleo-friendly options at restaurants or adapting recipes for social events can be challenging. This can lead to feelings of exclusion or difficulty participating in social activities with friends and family who are not following the same dietary restrictions.
Open communication with social circles and finding creative ways to adapt paleo principles to social situations can help mitigate this potential risk.
Unrealistic Expectations and Emotional Distress
The paleo diet, like any dietary approach, can sometimes be associated with unrealistic expectations regarding rapid or dramatic improvements in health. The focus on eliminating certain food groups can sometimes lead to feelings of deprivation or restriction, which may negatively impact emotional well-being if not managed appropriately. It's important to approach the diet with a realistic and balanced perspective, focusing on gradual improvements in health and well-being rather than quick fixes.
Potential for Imbalance in Macronutrients
While the Paleo diet emphasizes whole, unprocessed foods, it's crucial to ensure a balanced intake of macronutrients (carbohydrates, proteins, and fats). Inadequate attention to macronutrient ratios can lead to deficiencies in essential nutrients or an imbalanced energy intake. Without careful planning, individuals might inadvertently overconsume certain macronutrients or fall short of others, which can hinder weight management, energy levels, and overall health.
Difficulty in Long-Term Adherence
The strict nature of the paleo diet can make long-term adherence challenging for many individuals. The elimination of entire food groups can lead to feelings of restriction and monotony over time. Maintaining motivation and finding sustainable strategies for long-term adherence are crucial for achieving and sustaining any health goals. Developing a supportive network, incorporating enjoyable activities, and focusing on sustainable lifestyle changes can help enhance compliance with the paleo diet over the long term.
The Role of Gut Health and Autoimmune Conditions
The Gut Microbiome and Autoimmunity
The intricate relationship between the gut microbiome and autoimmune conditions is a burgeoning area of research. A healthy gut microbiome is essential for immune system regulation. This complex ecosystem of bacteria, fungi, and other microorganisms plays a crucial role in training and modulating the immune response. Disruptions in this delicate balance, often caused by dietary factors, environmental exposures, and even stress, can lead to an overactive immune response, potentially triggering or exacerbating autoimmune diseases. Understanding how dietary choices, particularly the Paleo diet, can influence this microbiome is critical in managing autoimmune conditions.
Studies suggest that an imbalance in the gut microbiome, often referred to as dysbiosis, is linked to various autoimmune diseases. This imbalance can manifest in the overgrowth of certain harmful bacteria or a deficiency of beneficial ones. The Paleo diet, by emphasizing whole, unprocessed foods and eliminating processed foods, refined sugars, and grains, aims to create a more favorable environment for a healthy gut microbiome. This approach focuses on providing nutrients and promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria, which could potentially help restore balance and mitigate the risk of autoimmune flare-ups.
The Paleo Diet and Gut Health Management
The Paleo diet, a dietary approach mimicking the purported diet of our Paleolithic ancestors, emphasizes whole, unprocessed foods like fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats. This approach generally excludes processed foods, grains, legumes, dairy, and refined sugars, which are often implicated in gut inflammation and dysbiosis. By removing these potentially inflammatory foods, the Paleo diet aims to reduce the burden on the digestive system and encourage the growth of a more robust and balanced gut microbiome.
Furthermore, the Paleo diet often promotes the consumption of high-fiber foods. Dietary fiber is essential for maintaining a healthy gut microbiome, providing nourishment for beneficial bacteria and promoting regularity. The emphasis on whole, unprocessed foods in the Paleo diet naturally provides a rich source of dietary fiber. This aspect of the diet plays a crucial role in supporting gut health, indirectly influencing the immune system's function and potentially reducing the likelihood of autoimmune flare-ups. However, it is important to note that individual needs and responses vary, and consulting with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian is crucial for personalized guidance.
The Paleo diet's focus on nutrient-dense foods can directly impact gut health by providing the necessary vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants for proper gut function. This approach often results in a reduction in processed foods and refined sugars, which can contribute to gut inflammation. By providing the body with the necessary building blocks, the Paleo diet may help to support a healthy gut environment, which in turn can aid in the management of autoimmune conditions.
Is the Paleo Diet Right for You?
Understanding the Paleo Diet
The Paleo diet, often touted as a way to improve health and well-being, emphasizes whole, unprocessed foods similar to what our Paleolithic ancestors supposedly consumed. This includes lean meats, fish, fruits, vegetables, and nuts. It typically excludes grains, legumes, dairy, and processed foods, aiming to eliminate foods thought to trigger inflammation and other health issues. Understanding the nuances of this approach, and how it might relate to autoimmune conditions, is crucial before considering adopting it.
A key aspect of the Paleo diet is its focus on nutrient-dense foods. This approach can lead to improved intake of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, potentially contributing to overall health. However, adhering strictly to the Paleo diet can also mean limiting certain important nutrients found in foods that are excluded, such as calcium from dairy or iron from legumes. This careful consideration is essential for any diet plan.
Potential Benefits for Autoimmune Conditions
Some individuals with autoimmune conditions report experiencing positive changes when following a Paleo diet. The reduced consumption of potentially inflammatory foods, like gluten and dairy, may alleviate symptoms for some. The emphasis on whole foods and lean proteins could also support overall well-being and contribute to a healthier immune system response. However, the mechanisms behind these potential benefits are not always clear and further research is needed.
The elimination of common allergens and inflammatory agents can potentially reduce flare-ups. This can contribute to a greater sense of control and improved quality of life. It is crucial, however, to remember that these benefits are not universally experienced, and individual responses vary significantly.
Potential Drawbacks and Considerations
While the Paleo diet may seem appealing for managing autoimmune conditions, there are potential drawbacks to consider. The strict elimination of entire food groups can lead to nutrient deficiencies if not carefully planned and monitored. This is particularly important for those with specific dietary needs or pre-existing health conditions. It's also important to ensure a diverse range of foods are being consumed to ensure adequate intake of all necessary nutrients.
Sustainability is another key factor. Adhering rigidly to the Paleo diet long-term might prove difficult for some individuals. The need for meticulous meal planning and potentially significant lifestyle adjustments can make it challenging to maintain consistency. Additionally, the lack of scientific evidence supporting the Paleo diet as a definitive treatment for autoimmune diseases needs to be acknowledged.
The Role of Professional Guidance
Before embarking on any significant dietary changes, especially for individuals with autoimmune conditions, consulting with a registered dietitian or a healthcare professional is crucial. A personalized approach is essential, considering individual needs and medical history. They can assess your specific health status, provide guidance on nutrient intake, and help you create a sustainable and balanced plan.
A healthcare professional can help identify potential risks and ensure that the dietary changes align with any existing medications or treatments. They can also monitor your progress and adjust the plan as needed to optimize your health and well-being. This comprehensive approach is paramount when managing autoimmune conditions.