Top 5 Healthy Fats You Should Be Eating
The Heart-Protecting Power of Monounsaturated Fats
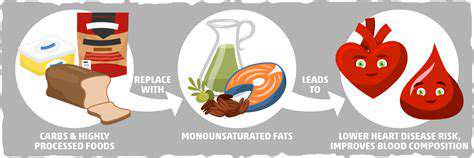
When it comes to maintaining cardiovascular wellness, monounsaturated fats stand as nutritional champions. These beneficial fats serve multiple essential functions - from building cell membranes to facilitating hormone synthesis. What makes them truly remarkable is their ability to lower harmful LDL cholesterol while maintaining good HDL levels, creating a protective shield for your heart.
The Mediterranean diet offers compelling evidence of these benefits, with olive oil-rich regions showing significantly lower heart disease rates. Research consistently demonstrates that swapping saturated fats for monounsaturated varieties leads to measurable improvements in cardiovascular markers. While these fats offer clear advantages, remember that balance remains fundamental - even the healthiest nutrients require mindful consumption.
Top Nutritional Sources for Heart Health
Nature provides an abundant variety of monounsaturated fat sources, each with unique health advantages:
- Extra virgin olive oil - The gold standard, packed with antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds
- Avocados - Creamy fruits offering fiber alongside their healthy fats
- Tree nuts - Almonds, cashews and pecans deliver protein and essential minerals
- Seeds - Pumpkin and sesame seeds provide crunch and nutrition
- Fatty fish - Certain varieties offer omega-3s along with monounsaturated fats
The key lies not just in consuming these foods, but in using them to replace less healthy fat sources in your diet. For instance, using avocado instead of mayonnaise or olive oil instead of butter can make a significant difference over time.
Whole-Body Benefits Beyond Cardiovascular Protection
The advantages of monounsaturated fats extend far beyond heart health. These versatile nutrients contribute to:
- Skin and hair vitality by maintaining cell membrane integrity
- Hormonal balance through their role in steroid hormone production
- Cognitive function as essential components of brain tissue
- Metabolic efficiency by enhancing nutrient absorption
Interestingly, these fats play a crucial role in weight management. Their slow digestion rate promotes satiety signals, helping curb between-meal cravings naturally. This makes them particularly valuable for those managing their weight without feeling deprived. When combined with their nutrient-transport capabilities, it's clear why monounsaturated fats deserve a prime spot in any balanced eating plan.
Saturated Fats: Finding the Right Balance
The Complex Nature of Saturated Fats
While often portrayed negatively, saturated fats actually play several important biological roles. These fats maintain cell membrane rigidity, support immune function, and aid in calcium absorption. The key insight modern nutrition science reveals is that different saturated fatty acids have varying metabolic effects, making blanket recommendations overly simplistic.
Primary Dietary Origins
Saturated fats naturally occur in:
- Animal products (beef, pork, dairy)
- Tropical oils (coconut, palm)
- Processed foods (often combined with refined carbs)
Interestingly, grass-fed animal products contain a different fatty acid profile than grain-fed versions, demonstrating how agricultural practices impact nutritional quality.
Cholesterol Dynamics and Individual Variability
The relationship between saturated fats and cholesterol proves more nuanced than commonly believed. While they can elevate LDL cholesterol, they often raise the large, buoyant LDL particles (less harmful) rather than the small, dense variety. Genetic factors significantly influence individual responses, with some people showing minimal cholesterol changes despite high intakes.
The Evolving Science of Heart Health
Recent meta-analyses suggest the heart disease risk from saturated fats may have been overstated. The context matters enormously - saturated fats consumed with refined carbohydrates and processed foods pose greater risk than those eaten in whole food matrices. This highlights the importance of considering overall dietary patterns rather than isolated nutrients.
Practical Consumption Guidelines
For optimal health:
- Prioritize whole food sources over processed versions
- Balance with monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats
- Consider your individual health status and genetics
- Focus on overall diet quality rather than single nutrients
The most current research supports a food matrix approach - evaluating how fats interact with other components in specific foods rather than judging them in isolation.