The Benefits of Eating Organic: A Deep Dive
Cardiovascular Health
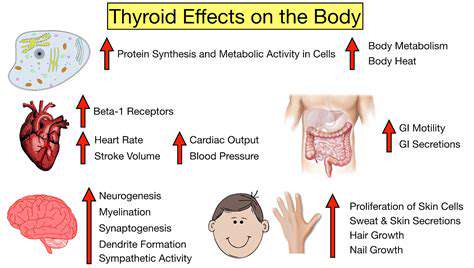
A strong cardiovascular system forms the foundation of overall wellness. Incorporating a variety of fresh produce and whole grains into one's diet has been shown to positively influence blood pressure and cholesterol markers, thereby decreasing the likelihood of cardiovascular events. Engaging in consistent physical movement, whether through walking, aquatic exercises, or bicycling, enhances cardiac performance and promotes efficient blood flow throughout the body.
Metabolic Function
The body's metabolic processes involve intricate mechanisms that transform nutrients into usable energy. Maintaining nutritional balance and staying physically active proves indispensable for proper metabolic regulation, weight management, and prevention of metabolic disorders. The strategic consumption of proteins, complex carbohydrates, and beneficial fats supports these vital biological functions.
Mental Well-being
Physical health and psychological wellness share an intimate connection. Nutritional choices, movement patterns, and sleep quality collectively influence stress resilience, emotional balance, and cognitive sharpness. These factors contribute to enhanced life satisfaction and improved capacity to navigate life's complexities. Notably, psychological health reciprocally impacts physical condition.
Immune System Support
Effective immune function serves as the body's primary defense against pathogens. Consuming nutrient-dense foods abundant in vitamins and antioxidants, combined with restorative sleep and regular activity, strengthens immunological responses. Additional protective measures include maintaining appropriate body weight and implementing stress reduction techniques.
Bone Health
Skeletal integrity becomes increasingly important throughout the lifespan. Dairy items, dark leafy greens, and fortified products provide essential nutrients for maintaining bone mineral density. Weight-bearing physical activities like walking or running stimulate osteogenesis, enhancing structural stability.
Digestive Health
Optimal gastrointestinal function underpins systemic health. Fermented foods containing beneficial bacteria support intestinal microbial balance, which enhances nutrient assimilation and digestive comfort. Adequate fluid intake and stress management techniques further promote gastrointestinal regularity.
Ethical Considerations: Supporting Sustainable and Humane Practices

Transparency and Openness
Clear disclosure of research methodologies and potential limitations represents a fundamental ethical obligation. Investigators should thoroughly document their procedures, acknowledge possible biases, and disclose funding sources to maintain academic integrity. Making research findings publicly accessible facilitates peer review and collaborative advancement. Properly informing participants about study objectives, procedures, and their rights establishes trust and ensures ethical compliance.
Respect for Persons and Privacy
Safeguarding participant confidentiality remains paramount in ethical research. Implementing robust data protection measures and obtaining comprehensive informed consent demonstrates respect for individual autonomy. Special considerations should be made for vulnerable populations, ensuring their protection from potential exploitation while providing necessary support systems.
Beneficence and Non-Maleficence
Research endeavors must carefully balance potential benefits against possible risks. Conducting thorough risk assessments and developing contingency plans demonstrates responsible research practice. Researchers must remain vigilant for unforeseen consequences and be prepared to implement corrective measures when necessary.
Justice and Equity
Ethical research requires fair distribution of both benefits and burdens. Conscious efforts must be made to prevent research practices from reinforcing existing social disparities. Particular attention should be paid to marginalized groups, ensuring their equitable participation and benefit from research outcomes while protecting them from potential harm.
Economic Benefits: Supporting Local Farmers and Communities
Supporting Local Farms
Purchasing from regional agricultural producers generates direct economic stimulation. These transactions circulate capital within the community, supporting ancillary businesses and creating employment opportunities across multiple sectors. The economic multiplier effect extends beyond agricultural production to include processing, distribution, and retail operations.
Enhanced Food Security
Regional agricultural systems demonstrate greater resilience to external disruptions. Diversified local producers can better adapt to environmental changes and market volatility, ensuring more consistent food availability and reducing dependence on distant supply chains.
Improved Food Quality and Safety
Proximity to food sources allows for better oversight of production methods. Regional farmers frequently employ sustainable practices that enhance nutritional quality while minimizing chemical inputs, providing consumers with greater confidence in their food choices.
Community Bonding and Engagement
Direct interactions between consumers and producers at local markets foster social connections and shared values. These exchanges strengthen community identity and promote appreciation for regional agricultural heritage.
Environmental Benefits
Reduced transportation requirements for locally-sourced foods decrease fossil fuel consumption and associated emissions. Regional food systems typically generate less packaging waste and have a smaller overall ecological footprint.
Economic Diversification
A robust local agricultural sector contributes to economic stability by providing multiple revenue streams and employment options. This diversification enhances community resilience against economic downturns in specific industries.
Boosting Local Businesses
The positive economic impacts of supporting regional agriculture extend to complementary enterprises. Increased demand for local products stimulates growth across various business sectors, creating new entrepreneurial opportunities and strengthening the overall economic landscape.