The Importance of Protein for Active Lifestyles

Protein's Impact on Metabolic Health
Protein significantly influences metabolic regulation, affecting how the body processes energy and nutrients. Its effects extend far beyond muscle tissue, impacting critical metabolic functions including fat metabolism and glucose regulation. This broader metabolic role emphasizes protein's importance for comprehensive health maintenance.
Research indicates that higher protein consumption can enhance metabolic efficiency, potentially supporting weight control and reducing risk factors for metabolic conditions like type 2 diabetes. The filling nature of protein-rich meals also contributes to better appetite management, helping individuals maintain healthier eating patterns.
Protein's Role in Satiety and Appetite Control
Protein stands out for its remarkable ability to promote prolonged fullness. Compared to carbohydrates or fats, protein provides superior satiety, naturally reducing overall calorie consumption. This sustained satisfaction can be invaluable for weight management and preventing excessive food intake.
This satiating effect stems from protein's interaction with hunger-regulating hormones. It effectively signals the brain to reduce hunger sensations, creating a natural mechanism for controlled eating. Understanding this relationship provides powerful tools for sustainable weight management strategies.
Protein's Influence on Blood Sugar Regulation
Protein plays a critical role in maintaining stable blood sugar levels. When consumed with carbohydrates, protein slows glucose absorption, preventing dangerous blood sugar spikes. This benefit proves particularly valuable for individuals managing diabetes or seeking to maintain consistent energy levels.
The amino acids from protein contribute to producing essential enzymes and hormones involved in glucose metabolism. This regulated glucose release supports sustained energy and protects against metabolic imbalances, highlighting protein's importance in comprehensive health management.
Protein's Contribution to Muscle Repair and Growth
As the primary structural component of muscle tissue, protein remains indispensable for exercise recovery. Physical activity creates microscopic muscle damage, requiring protein for effective repair and subsequent strength development. Optimal protein availability directly influences the success of any training program.
The muscle protein synthesis process depends entirely on amino acid availability from dietary protein. This complex biological mechanism underscores the importance of quality protein sources for anyone pursuing fitness goals or maintaining muscle mass.
Protein's Impact on Hormone Production
Protein serves as a fundamental resource for hormone synthesis, affecting numerous bodily systems. These chemical messengers regulate metabolism, hunger signals, stress responses, and other critical functions. Maintaining adequate protein intake proves essential for balanced hormone production and overall physiological harmony.
Given the complexity of endocrine function, protein's role as a building block for hormones positions it as a crucial dietary component for maintaining multiple aspects of health and wellbeing.
Protein's Role in Bone Health
Protein's benefits extend significantly to skeletal strength and durability. Appropriate protein consumption supports bone formation and maintenance, helping prevent osteoporosis and fractures, particularly in aging populations. This aspect of protein's function deserves equal attention to its muscular effects.
By contributing to bone density and structural integrity, protein plays a vital role in maintaining mobility and reducing fracture risk throughout life. This underscores protein's comprehensive value in long-term health maintenance.
Protein Sources and Dietary Considerations
Diverse protein options exist, ranging from animal products to plant-based alternatives. Including varied sources ensures complete amino acid profiles and balanced nutrition. A strategic combination of different protein foods forms the foundation of optimal dietary patterns.
Personal dietary requirements and preferences should guide protein source selection. Professional nutritional advice can help tailor protein choices to individual health objectives and lifestyle considerations.
Choosing the Right Protein Sources for Your Needs

Understanding Your Protein Needs
Determining personalized protein requirements represents a critical step in health and fitness planning. Multiple factors including age, activity patterns, and health status influence ideal protein consumption levels. Professional nutritional assessment provides the most accurate guidance for meeting individual protein needs without excess or deficiency.
Recognizing protein's fundamental role in tissue maintenance and repair proves especially important for physically active individuals. The body's constant regeneration processes demand consistent protein availability for optimal functioning.
Animal-Based Protein Sources
Animal-derived proteins typically provide complete amino acid profiles along with additional nutrients. Meats, poultry, fish, and eggs deliver high-quality protein alongside essential vitamins and minerals like iron and B vitamins. These nutrient-dense options support multiple aspects of health beyond muscle maintenance.
Lean beef cuts offer particularly rich protein content along with important minerals. When consumed as part of balanced nutrition, these animal products can significantly contribute to meeting comprehensive dietary needs.
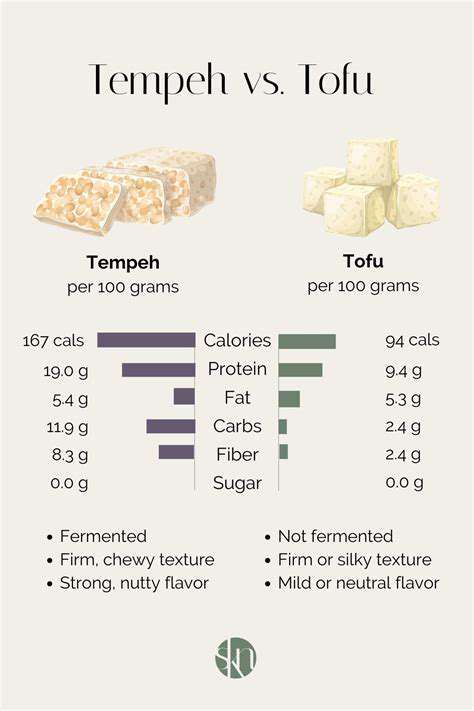
Plant-Based Protein Sources
Plant proteins, while sometimes incomplete, offer valuable nutritional contributions. Legumes provide excellent protein and fiber content, supporting digestive health and sustained energy. These versatile foods also deliver various micronutrients beneficial for overall wellbeing.
Soy-based products represent complete plant proteins, making them particularly useful for vegetarian and vegan diets. Their adaptability in cooking allows for creative incorporation into diverse meal plans while maintaining nutritional value.
Processed Meats and Their Impact
While processed meats contain protein, their consumption requires careful consideration. Products like sausages and bacon often contain excessive sodium, saturated fats, and preservatives. Regular overconsumption may contribute to developing chronic health conditions, warranting moderation in dietary planning.
Prioritizing fresh, minimally processed protein sources generally provides superior health benefits while reducing potential risks associated with processed alternatives.
Dairy Products and Their Nutritional Value
Dairy foods serve as excellent protein sources while providing additional bone-supporting nutrients. Milk, yogurt, and cheese offer complete proteins alongside calcium and vitamin D. Fermented dairy products like yogurt also deliver beneficial probiotics for gut health support.
These readily available options provide convenient protein solutions, though individuals with lactose sensitivity should explore suitable alternatives to meet their nutritional needs.
Protein Supplements: Benefits and Considerations
Protein powders can assist individuals struggling to meet requirements through whole foods alone. Various types including whey, casein, and plant-based powders offer different absorption characteristics. These supplements can be incorporated creatively into shakes or recipes to boost protein intake conveniently.
However, supplements should enhance rather than replace balanced nutrition. Professional guidance helps ensure appropriate use without creating nutritional imbalances or overlooking other dietary needs.