The Connection Between Diet and Chronic Fatigue
Macronutrients are essential components of our diet, providing the body with the energy it needs to function. They are the building blocks of our cells and tissues, supporting various bodily processes. Understanding their importance is crucial for maintaining a healthy lifestyle and achieving specific fitness goals.
These vital nutrients are categorized into carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Each plays a unique role in fueling the body, and deficiencies in any of these can lead to a range of health issues. A balanced intake of all three is paramount for optimal health.
Carbohydrates: The Body's Primary Energy Source
Carbohydrates are the body's primary source of energy. They are broken down into glucose, which is then used to fuel bodily functions, including physical activity and brain activity. Complex carbohydrates, found in whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, provide sustained energy release. Simple carbohydrates, found in sugary drinks and processed foods, can lead to rapid spikes in blood sugar levels.
Consuming adequate amounts of carbohydrates is essential for maintaining energy levels throughout the day. A diet lacking in carbohydrates can result in fatigue and decreased performance.
Proteins: Building Blocks of the Body
Proteins are the building blocks of our bodies, playing a crucial role in tissue repair, growth, and maintenance. They are essential for building and repairing muscles, organs, and other tissues. Amino acids, the building blocks of proteins, are essential for various bodily functions.
Proteins are also involved in hormone production and immune function. A sufficient intake of protein is important for maintaining muscle mass, which is critical for strength and metabolism. Sources of protein include meat, poultry, fish, eggs, beans, and legumes.
Fats: Essential for Various Body Functions
Fats are essential for various bodily functions, including hormone production, nutrient absorption, and insulation. They provide a concentrated source of energy and help to protect vital organs. Healthy fats, such as those found in avocados, nuts, and olive oil, are crucial for optimal health.
Unsaturated fats are beneficial for heart health and overall well-being. However, it's important to be mindful of saturated and trans fats, which can negatively impact cholesterol levels and increase the risk of heart disease. A balanced intake of different types of fats is important.
Macronutrient Ratios for Optimal Health
The ideal macronutrient ratios can vary depending on individual needs and goals. For general health, a balanced intake of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats is recommended. However, athletes or individuals with specific dietary needs may require different ratios.
Understanding the ratios and proper intake amounts is key to achieving optimal health and well-being. Consulting a registered dietitian or nutritionist can provide personalized recommendations based on individual circumstances.
Macronutrients and Dietary Considerations
Dietary considerations can significantly impact macronutrient intake. For example, individuals with diabetes may need to carefully manage their carbohydrate intake. Individuals following a vegetarian or vegan diet need to ensure they are getting adequate protein sources from plant-based foods.
Diverse dietary needs require careful planning and consideration. It is crucial to choose foods that provide the necessary nutrients in the desired amounts and proportions. Always consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian for personalized dietary advice.
The Impact of Micronutrients and Deficiencies
Micronutrient Importance in Overall Health
Micronutrients, though present in smaller quantities than macronutrients, play a vital role in numerous bodily functions. They act as catalysts for enzyme reactions, support immune function, and contribute to healthy cell growth and development. These essential vitamins and minerals are often overlooked, but their absence can lead to a cascade of health issues, impacting everything from energy levels to cognitive function. Understanding the significance of these vital components is crucial for maintaining optimal well-being and preventing deficiencies that can contribute to chronic conditions.
The body needs a balanced intake of various micronutrients to function correctly. Each nutrient plays a specific role, from supporting the immune system to aiding in energy production. A deficiency in any one of these crucial micronutrients can have far-reaching consequences, potentially leading to fatigue, impaired immunity, and an increased susceptibility to various diseases. The interconnectedness of these nutrients within the body highlights the importance of a varied and balanced diet for overall health.
Deficiencies and Their Potential Impact on Chronic Conditions
Nutrient deficiencies can significantly impact the development and progression of chronic diseases. For example, iron deficiency can lead to anemia, impacting energy levels and cognitive function. Vitamin D deficiency has been linked to an increased risk of chronic diseases like type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular issues. Furthermore, deficiencies in other crucial micronutrients can contribute to weakened immune function, making individuals more susceptible to infections and potentially hindering the body's ability to fight chronic diseases effectively.
The long-term effects of these deficiencies can be substantial, contributing to the development of chronic conditions. A consistent lack of essential nutrients can disrupt cellular processes, impacting organ function and overall health. Recognizing the link between micronutrient deficiencies and chronic diseases is vital for implementing preventative measures and promoting well-being. Addressing nutritional gaps through dietary modifications and supplementation can be crucial for mitigating the potential impact of these deficiencies on the development and progression of chronic conditions.
Dietary Strategies for Micronutrient Intake
A diet rich in a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins is crucial for obtaining adequate micronutrients. Consuming a rainbow of fruits and vegetables provides a broad spectrum of vitamins and minerals. Choosing whole grains over refined grains ensures a more complete nutrient profile, including vital B vitamins and minerals. Incorporating lean proteins, such as fish, poultry, and beans, provides essential amino acids and contributes to the overall nutritional balance.
Furthermore, understanding portion sizes and the nutritional content of different foods can help individuals make informed choices. Reading food labels and consulting with a registered dietitian or healthcare professional can provide valuable insights into personalized dietary strategies for micronutrient intake. This knowledge allows individuals to address potential deficiencies and create a more effective approach to achieving optimal health and preventing future chronic health problems.
The Role of Supplements in Addressing Deficiencies
In some cases, dietary modifications alone may not be sufficient to address micronutrient deficiencies. Consulting with a healthcare professional about appropriate supplementation can be beneficial in certain situations. Supplements can provide a concentrated dose of specific nutrients, addressing potential gaps in dietary intake. However, it's crucial to remember that supplements should be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional. Self-treating with supplements without proper guidance could potentially lead to imbalances and adverse effects.
Individual needs vary, and a healthcare professional can assess an individual's specific nutritional requirements and recommend appropriate supplements. This personalized approach ensures that supplements are used effectively and safely, maximizing their potential benefits without causing harm. It's important to approach supplementation as part of a broader strategy for improving overall health, rather than as a standalone solution.
The Importance of Hydration and Digestive Health
Hydration and Digestive Function
Maintaining adequate hydration is crucial for optimal digestive health. Water acts as a lubricant, facilitating the smooth movement of food through the digestive tract. Insufficient water intake can lead to constipation, a common digestive issue, as stool becomes hard and difficult to pass. Proper hydration also supports the production of digestive enzymes and saliva, which are essential for breaking down food and initiating the digestive process. This, in turn, can reduce strain on the digestive system and promote a healthier overall gut environment.
The volume of water needed varies based on individual factors like activity level and climate. However, a general guideline is to drink plenty of water throughout the day. This includes not only plain water but also hydrating beverages like unsweetened tea and broth. Pay attention to your body's signals; thirst is a reliable indicator of dehydration, and it's important to address it promptly.
Dietary Fiber and Gut Health
A diet rich in dietary fiber is essential for a healthy digestive system. Fiber acts as a prebiotic, feeding beneficial gut bacteria that play a vital role in digestion, immunity, and overall well-being. These beneficial bacteria ferment fiber, producing short-chain fatty acids, which nourish the cells lining the colon and help maintain a healthy gut microbiome. Include a variety of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains in your diet to ensure adequate fiber intake.
Digestive Enzymes and Nutrient Absorption
Digestive enzymes are crucial for breaking down food into smaller, absorbable molecules. Without sufficient enzyme production or if the enzymes are impaired, the body struggles to extract nutrients from food. This can lead to nutrient deficiencies and various health problems. A balanced diet rich in protein, as well as certain fruits and vegetables, often provides the raw materials for the body to produce digestive enzymes.
Certain foods and conditions can impact enzyme production and function. For example, excessive consumption of processed foods, high in sugar and fat, can negatively affect enzyme production. Chronic stress and inflammation can also impair enzyme activity. Understanding these factors can help you make informed dietary choices for a healthier digestive system.
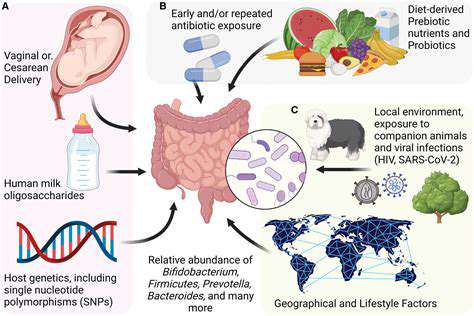
Probiotics and Prebiotics for Gut Balance
Probiotics and prebiotics are live microorganisms and non-digestible food ingredients, respectively, that support the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut. A healthy balance of these bacteria is essential for optimal digestion, immunity, and overall well-being. Probiotics can be found in fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, and sauerkraut. Prebiotics are found in foods like bananas, onions, and garlic.
Incorporating probiotics and prebiotics into your diet can help restore a healthy gut microbiome and improve digestive function. However, it's essential to consult with a healthcare professional before introducing significant changes to your diet, especially if you have underlying health conditions.
AI-powered automation extends far beyond basic tasks, offering a transformative leap in operational efficiency. By analyzing vast datasets and identifying patterns, AI can optimize processes and workflows in previously unimaginable ways. This enhanced efficiency translates directly into cost savings and increased productivity across diverse industries.
The Effects of Processed Foods and Sugar Intake

Processed Foods and Their Impact on Health
Processed foods are ubiquitous in modern diets, often appealing due to their convenience and extended shelf life. However, the extensive processing involved frequently leads to significant nutritional changes and often results in a product with reduced nutritional value compared to its unprocessed counterpart. The high sodium, sugar, and unhealthy fats often present in these foods contribute to a multitude of health concerns.
The Role of Sugar in Processed Foods
The high sugar content in many processed foods is a major concern for public health. This added sugar can lead to weight gain, impacting overall health and increasing the risk of chronic diseases like type 2 diabetes and heart disease. Furthermore, excessive sugar intake can disrupt the body's natural metabolic processes, potentially leading to long-term health complications.
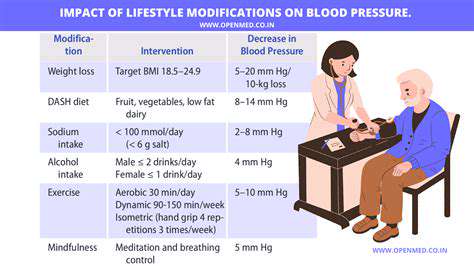
Sodium Content and Blood Pressure
Processed foods are frequently high in sodium, a crucial mineral for the body, but often present in levels exceeding the recommended daily intake. Excessive sodium intake can lead to elevated blood pressure, a significant risk factor for cardiovascular diseases. This elevated pressure puts stress on the heart and blood vessels, potentially leading to serious health consequences.
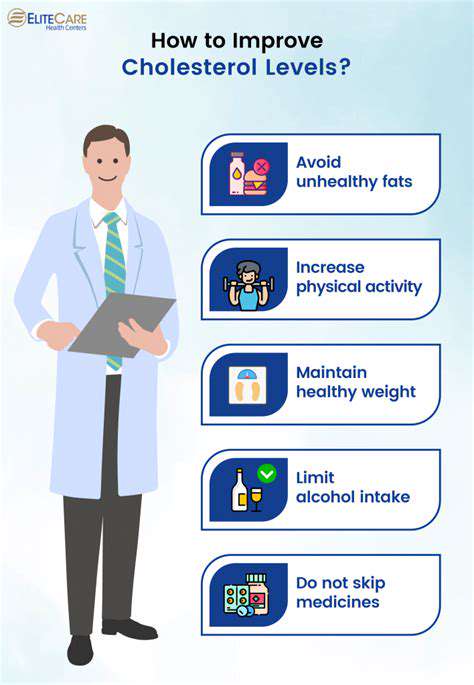
Hidden Fats and Their Consequences
Many processed foods contain significant amounts of unhealthy fats, often in the form of saturated and trans fats. These fats can contribute to the buildup of cholesterol in the arteries, narrowing the blood vessels and increasing the risk of heart disease. This contributes to the development of cardiovascular issues and long-term health problems.
The Nutritional Value Trade-off
The extensive processing methods used to produce many processed foods often result in a significant loss of essential vitamins, minerals, and dietary fiber. These essential nutrients are crucial for maintaining overall health and well-being. The lack of these vital nutrients can lead to deficiencies that impact various bodily functions. This nutritional compromise can negatively affect long-term health and well-being.
Potential Impacts on Mental Health
The connection between diet and mental health is increasingly recognized. Studies suggest a potential link between the consumption of processed foods and an increased risk of mental health challenges. The high levels of sugar and unhealthy fats in these foods can disrupt the body's natural processes, possibly affecting mood regulation and cognitive function. The impact of these foods on mental health warrants further research.
Addressing Underlying Conditions and Seeking Professional Advice

Identifying the Root Cause
Understanding the root cause of a problem is paramount to effective solutions. A thorough investigation into the underlying conditions often reveals interconnected factors that contribute to the issue. This process requires careful analysis and a willingness to consider various perspectives, recognizing that the problem may not be as straightforward as it initially appears. Addressing the root cause, rather than merely treating symptoms, is crucial for long-term success and preventing recurrence.
Often, symptoms are simply outward manifestations of deeper issues. Ignoring the root cause can lead to ineffective and ultimately unsustainable solutions. A systematic approach, incorporating diverse input and data analysis, is critical to pinpoint the core problems that require attention.
Analyzing Impact on Key Areas
Considering the broader implications of the underlying condition is vital. This involves evaluating how it affects various facets of the system or organization, from individual performance to overall productivity. A comprehensive analysis must identify the extent of the impact on different stakeholders and the potential for cascading effects.
This analysis requires gathering data from different sources and perspectives, including those directly and indirectly affected by the condition. Understanding the ripple effect of the problem will allow for a more holistic and effective strategy for intervention.
Developing Targeted Solutions
Once the root cause and its impact are understood, the next step is to develop targeted solutions. These solutions should be tailored to the specific needs and context of the problem, taking into account the unique factors involved. A one-size-fits-all approach is unlikely to be effective, and a more nuanced and individualized strategy is needed.
Implementing and Monitoring Solutions
Implementing the developed solutions requires a clear plan of action, outlining specific steps and timelines. Effective implementation also involves clear communication and collaboration among stakeholders to ensure smooth execution and buy-in. Successful implementation often depends on strong leadership and a commitment to follow-through.
Ongoing monitoring is critical to assess the effectiveness of the implemented solutions. Regular evaluation and feedback mechanisms are essential to identify any emerging issues and make necessary adjustments to the strategy.
Evaluating and Adapting Strategies
Evaluation of implemented solutions must be thorough and objective. This involves measuring the impact of the interventions against predefined metrics and benchmarks. Comparing the results to the initial goals and objectives will determine the degree of success and identify areas for improvement.
Adaptability is key. If the initial solutions prove inadequate, the strategy must be adaptable to evolving circumstances and new information. A flexible approach allows for course correction, fine-tuning, and refinement of the solution as needed.
Long-Term Sustainability
Achieving long-term sustainability requires a focus on preventative measures and proactive problem-solving. This entails identifying potential future challenges and developing strategies to mitigate them. Developing resilient systems and processes is crucial to prevent recurring issues and maintain the effectiveness of the solutions implemented.
This proactive approach requires ongoing commitment and investment in preventative measures to ensure the long-term viability and success of the implemented solutions.